文章目录
Spring框架的Web项目中可以使用properties文件来存储需要显示在jsp页面的一些值,比如label值或者error messages。然后通过Spring提供的ResourceBundleMessageSource将这些properties文件注入进来使用。一个简单的配置如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>labels</value>
<value>errors</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
|
而在我们的项目中有这样一个需求。假设现在项目中有三个properties文件。
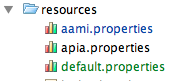
其中aami和apia是我们项目需要支持的两个品牌。当一个用户登陆我们的web项目时,会自动将其当前所使用的品牌信息存到session中。而如果是aami用户的话,前端jsp页面显示的message读取的顺序是这样的:如果在aami.properties文件中没找到的话,就在default.properties文件中找。对于apia用户,则先在apia.properties中找,然后查找default.properties。
举个例子,如果default.properties中有一个键值对helloWorld.label = Welcome。那么在jsp上使用时会显示Welcome。但是对于ammi来说需要用同样的键hello.world.label但是显示Welcome to AAMI。
这样可以最大程度的复用default.properties中的数据,同时又可以根据自身品牌定义一些自身的数据在自身品牌的properties文件中。
ResourceBundleMessageSource中有一个parentMessageSource属性,如果在当前MessageSource中找不到code的值,会在parentMessageSource中查找。一个简单的配置如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="parentMessageSource">
<bean class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename">
<value>default</value>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>aami</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
|
如果给给定一个code,程序会先在aami.properties文件中查找,如果未找到,则会在default中查找。
这似乎能满足我们的要求。其实不行。假如我们现在将apia品牌也加入,如果想让程序根据当前用户的品牌来选择适合的properties做成首选,当前这个功能是不满足的。我们需要自定义一个继承自ResourceBundleMessageSource的类来实现。
SessionMessageSource.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
public class SessionMessageSource extends ResourceBundleMessageSource {
static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SessionMessageSource.class);
private String[] basenames = new String[0];
@Override
protected String resolveCodeWithoutArguments(String code, Locale locale) {
ServletRequestAttributes attr = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
final String brand = (String) attr.getAttribute("brand", RequestAttributes.SCOPE_SESSION);
logger.debug(brand);
ArrayList<String> basenameList = Lists.newArrayList(basenames);
for(String basename : basenameList) {
if (StringUtils.endsWithIgnoreCase(basename,brand)) {
ResourceBundle bundle = getResourceBundle(basename, locale);
if (bundle != null) {
return getStringOrNull(bundle, code);
}
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void setBasenames(String... basenames) {
if (basenames != null) {
this.basenames = new String[basenames.length];
for (int i = 0; i < basenames.length; i++) {
String basename = basenames[i];
Assert.hasText(basename, "Basename must not be empty");
this.basenames[i] = basename.trim();
}
}
else {
this.basenames = new String[0];
}
super.setBasenames(basenames);
}
private String getStringOrNull(ResourceBundle bundle, String key) {
try {
return bundle.getString(key);
}
catch (MissingResourceException ex) {
return null;
}
}
}
|
我们首先重写了setBeanNames方法。该方法用于在配置文件中注入properties文件。之所以在这里拿到basenames是为了在resolveCodeWithoutArguments方法中使用。如果父类暴露了basenames属性我们就无需在自己的类中再记录这个属性。
此类重写了父类中的resolveCodeWithoutArguments方法。父类中该方法的职责是在查找自身的ResourceBundle中是否能找到对应code的值,如果找不到就返回null。由于resolveCodeWithoutArguments方法是被getMessageInternal方法调用的。而getMessageInternal方法的大概职责是查看自身的ResourceBundle能否找到code值,否则查找parentMessageSource。所以我们只需对resolveCodeWithoutArguments动手术即可。
在这个方法中,我们首先获取存储在session中的brand值,根据brand值找到对应的propeties文件,使用ResourceBundle来读取code值,如果未找到则返回null,以委托给getMessageInternal来找寻父MessageSource。这样可以有效地将不同的brand隔离开来。
那么在xml中的配置如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<bean id="messageSource"
class="com.thoughtworks.config.SessionMessageSource">
<property name="parentMessageSource">
<bean class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename">
<value>default</value>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>aami</value>
<value>apia</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
|
此外还需要在适当的时候设置session。
StartFlowController.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Controller
public class StartFlowController {
@RequestMapping(value= "/aami", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String onAAMIPage(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getSession().setAttribute("brand", "aami");
return "redirect:aami/index";
}
@RequestMapping(value= "/apia", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String onAPIAPage(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getSession().setAttribute("brand", "apia");
return "redirect:apia/index";
}
}
|
这些代码可以在我的github中找到。地址是https://github.com/huangbowen521/SpringMessageSpike。